Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT) for Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss
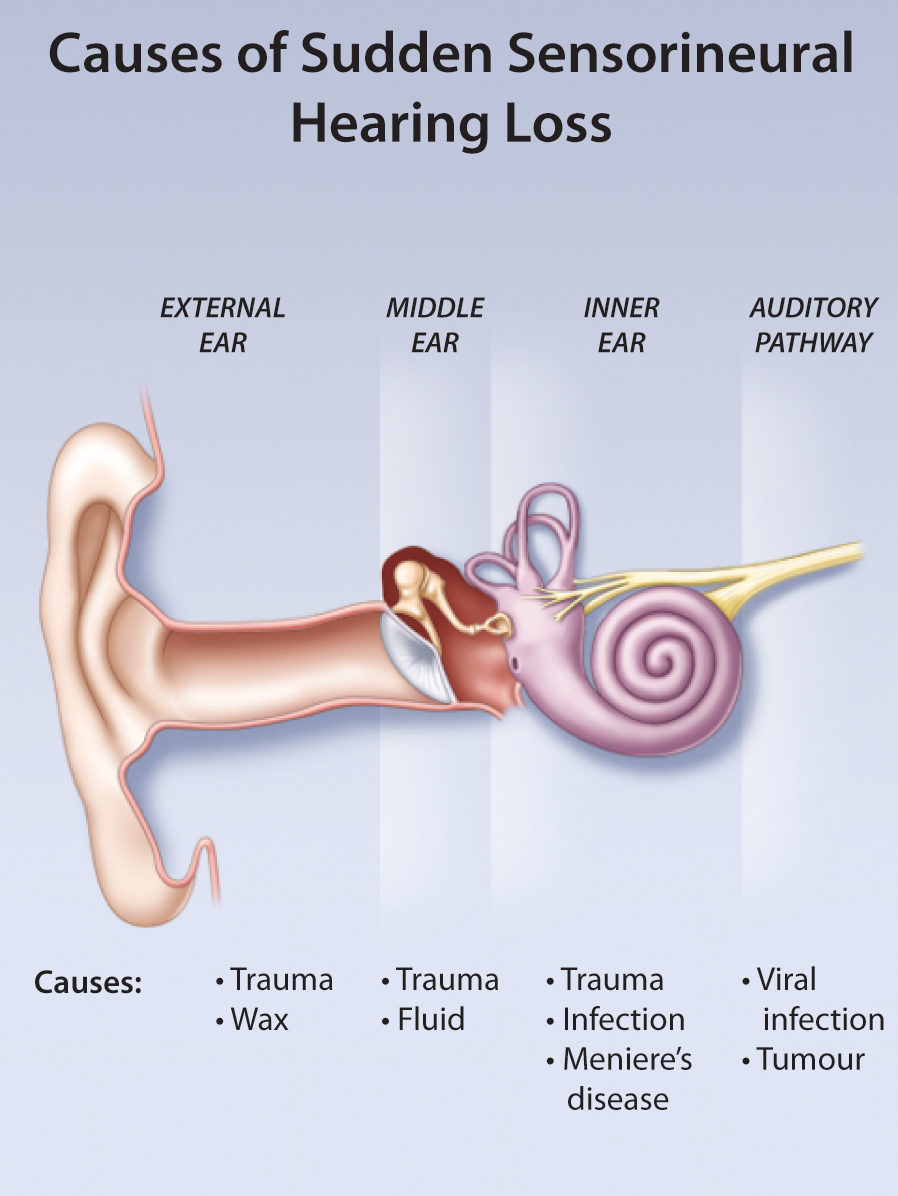
Sudden sensorineural hearing loss (SSHL) is also known as sudden deafness. It occurs when you lose your hearing very quickly, typically only in one ear. It can happen instantly or over a span of several days. During this time, sound gradually becomes muffled or faint.
The rationale for the use of hyperbaric oxygen thereapy (HBOT) to treat SSHL is supported by an understanding of the high metabolism and paucity of vascularity to the cochlea. The cochlea and the structures within it require a high oxygen supply. The direct vascular supply, particularly to the organ of Corti, is minimal. Tissue oxygenation to the structures within the cochlea occurs via oxygen diffusion from cochlear capillary networks into the perilymph and the cortilymph. The perilymph is the primary oxygen source for these intracochlear structures. Unfortunately, perilymph oxygen tension is decreased significantly in patients with SSHL. To achieve a consistent rise of perilymph oxygen content, the arterial-perilymphatic oxygen concentration difference must be extremely high. This can be restored with HBOT.
SSHL is a serious medical condition and requires prompt medical attention. Call your doctor right away if you think you’re experiencing SSHL. Early treatment can save your hearing.
*Although it is an approved indication by the undersea and medical society (UHMS), it may not be covered by insurance.